Hearing Loss
Get a hearing test with a specialist in Burlington – CALL US AT 905-635-HEAR (4327)
Hearing loss can be categorized into 3 types:
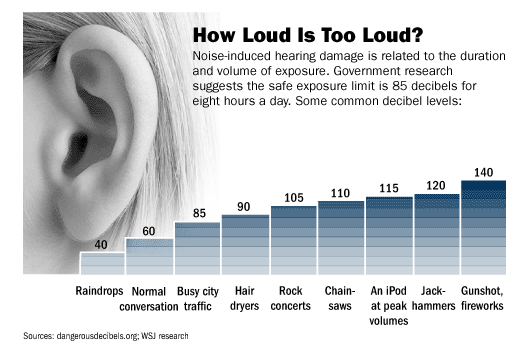
Contact us today if you’re concerned about hearing loss and would like to book a free hearing consultation with a specialist. Following a hearing test, our Doctor of Audiology at our hearing clinic in Burlington can provide a free hearing consultation, custom hearing instruments, and more.
